The EU-funded 5GSOLAR project seeks to advance Europe’s sustainable development and clean energy goals while supporting the European Research Area (ERA). It unites research, innovation, key stakeholders, policymakers, and society in photovoltaics. The project focuses on developing emerging materials for flexible photovoltaics, including designing advanced structures like tandem, concentrator, and bifacial solar cells using innovative antimony-based processing techniques.
Tandem solar cells
Tandem solar cells, with multiple stacked semiconductor layers, provide a promising way to boost efficiency for high-performance photovoltaics. By combining several semiconductor junctions, these cells capture a broader solar spectrum, leading to higher conversion efficiencies.
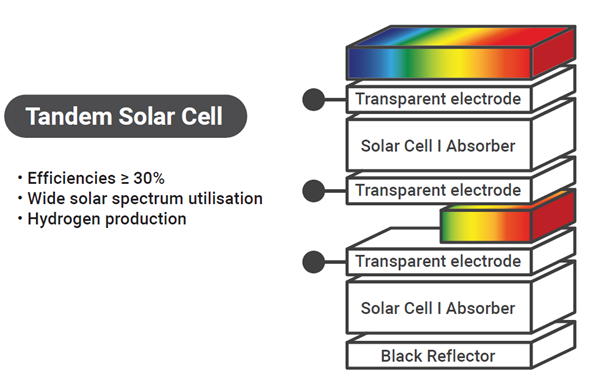
Tandem solar cells (SCs) with III-V semiconductor multi-junctions have achieved up to 38.8% efficiency, mainly in space applications. Thin-film tandem approaches like CIGSSe/CIS, CdTe/CIS, and Si/perovskite have reached about 20% efficiency. A key challenge in developing silicon tandem cells is proving that adding a sub-cell with green, abundant, cost-effective materials can match or exceed multi-junction performance.
The 5GSOLAR project addresses this with two strategies: first, creating a two-cell Sb2Se3/Sb2S3 stack that leverages the ideal bandgap values; second, exploring a Si/Sb2S3 tandem configuration using mechanical stacking for cost-effectiveness and design flexibility.
Bifacial solar cells
Bifacial solar cells capture light from both the front and rear, converting indirect light like ground-reflected albedo radiation. This can increase power conversion by over 30%, and up to 50% with solar tracking, compared to monofacial cells, without needing extra space. This technology is highly effective in Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) and is used in sound barriers and 3D installations.
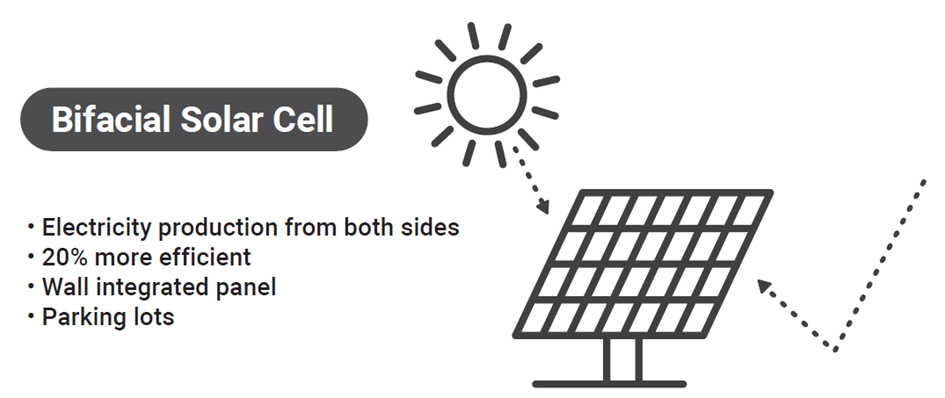
Bifacial technology’s market share is set for significant growth, projected to rise from under 5% in 2018 to nearly 40% by 2028, according to the International Roadmap of Photovoltaics. Silicon technology has effectively leveraged bifacial benefits, while other bifacial cells like thin-film CdTe, CIGSSe, dye-sensitized, and perovskites are being explored for flexible, lightweight, and semitransparent uses. A key challenge for the 5GSOLAR project is developing green, abundant, and efficient photovoltaic materials for these technologies.
These advancements also cater to the Internet of Things (IoT), especially with 5G, by connecting numerous devices to autonomous power supplies, promoting efficient and sustainable operation.

Sb-chalcogenide material shows great potential as an indoor light harvester due to its optimized transmission-absorption spectrum. The growth of bifacial technology in power plants and the expanding rooftop market, which prioritizes safety, is expected to boost module-level power electronics. With high-efficiency cells enabling bifacial power generation, this technology is poised to gain significant market share, aligning with the goals of the 5GSOLAR project.
The goal
The research aims to develop stable, highly efficient Sb-based solar cells with controllable transparency. To achieve this, the team is enhancing its skills through recruitment, development, and specialized training. An expanding international cooperation network supports these efforts. The business environment is also actively engaged, aiming for the successful practical application of the project’s outcomes.

